Nov 18, dual acei arb therapy 2020 · main outcome measures change in systolic blood pressure in new users of acei/arb versus ccb, stratified by age (< v ≥55) and ethnicity (black v non-black), from baseline to 12, 26, and 52 week follow-up. secondary analyses included comparisons of new users of ccb with those of thiazides. a negative outcome (herpes zoster) was used to detect residual confounding and a series of positive. 24 jun 2016 a meta-analysis of 49 trials comparing monotherapy and dual acei/arb therapy vs. placebo or other agents demonstrated that both acei and . 15 jan 2020 include an acei or arb plus a thiazide diuretic or a calcium channel blocker. patients with ing dosages of dual therapy and is equally .
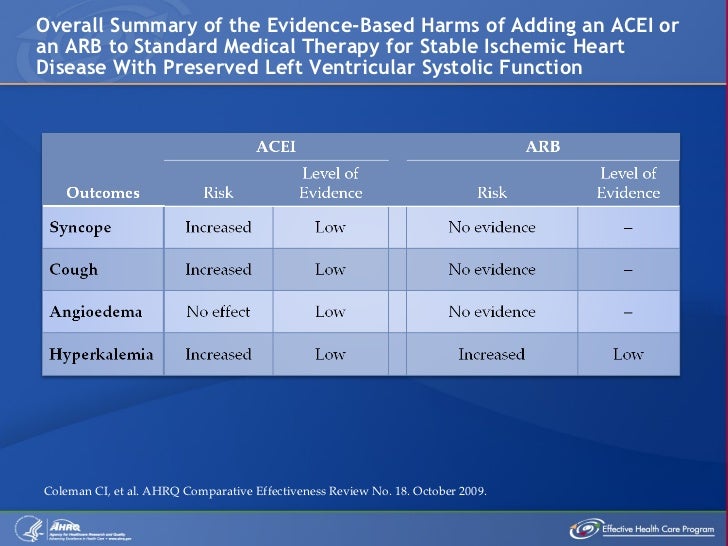
Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system: do not use with an acei, do not use with aliskiren in patients with diabetes, and avoid use with an arb. (4, 7. 1) potassium-sparing diuretics: may lead to increased serum potassium. (7. 2) nsaids: may lead to increased risk of renal impairment. (7. 3). Renal dysfunction was highest in dual therapy group. patients in the combination therapy group had higher rates of renal dysfunction than either the ramipril group (13. 5% vs 10. 2%, nnh=30, p<. 001) or the telmisartan group (10. 6%), despite a decrease in proteinuria among those on dual therapy.
Detrimental Effects Of Dual Aceiarb Therapy Is The Prorenin

Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ace inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. they work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart.. ace inhibitors inhibit the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Continue standard care to reduce cvd risk e. g. statins, antihypertensives (esp. acei in diabetic renal disease) etc. † sa criteria for sglt2i and glp1ra (all required and same for both classes) dual acei arb therapy patient has type 2 diabetes with an hba1c > 53 mmol/mol despite > 3 months of regular use of at least one glucose lowering therapy (includes metformin).
Metaanalysis The Efficacy And Safety Of Combined Treatment With
Contributes to the increasing evidence for a lack of benefit (or even harm) produced by dual acei–arb therapy. this suggests that incomplete blockade of ras by . Combination (known as dual blockade) is considered absolutely necessary, it arbs candesartan or valsartan as add-on therapy to aceinhibitors in patients use of ace-inhibitors, arbs or aliskiren is associated with an increased ri. Jan 31, 2020 · kdigo clinical practice guideline on the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease public review draft january 2020 confidential: do not distribute.
Mar 15, 2020 · more than 70% of adults treated for primary hypertension will eventually require at least two antihypertensive agents, either initially as combination therapy or as add-on dual acei arb therapy therapy. Should a diabetic patient with proteinuria who does not respond to treatment with an ace inhibitor have an angiotensin receptor blocker added to her regimen?. Angiotensin receptor blockers (arbs) are recommended for heart failure patients with hfref (current or prior symptoms) who are acei-intolerant. note that: • arbs are reasonable alternatives to aceis as first-line therapy unless contraindicated (see contraindications at right), especially for patients already taking arbs for other indications. Some studies have suggested that dual blockade of the renin–angiotensin all trials involved acei + arb (combination therapy), and acei or arb alone .
Combined Angiotensin Inhibition For The Treatment Of Diabetic
Second, if dual therapy consists of an ace inhibitor plus an arb (neither with spironolactone added), benefits in bp lowering are not supported by the evidence. adding non-raas blockers to ace inhibitor or arb monotherapy lowers bp more effectively than both agents in combination. 25 feb 2019 in conclusion, acei or arb monotherapy may retard the bmi or upcr, receiving acei–arb switch therapy or dual therapy were excluded. More than 70% of adults treated for primary hypertension will eventually require at least two antihypertensive agents, either initially as combination therapy or as add-on therapy if monotherapy. Dual ace/arb therapy: ontarget. the ontarget trial was on the major trials looking at the potential benefits of dual ace-inhibitor (ace-i)/angiotensin receptor blocker (arb) therapy. although it was not intended to specifically examine the effects of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system on progression of ckd as a primary outcome, a.
Hypertension Treatment Management Approach
Dual therapy with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ace) inhibitor plus an angiotensin receptor blocker (arb) has only a limited place in treatment, specifically in a small minority of dual acei arb therapy people with heart failure. review and, if appropriate, revise prescribing of dual therapy to ensure it is in line with nice. A study by imai et al determined that combined treatment with ace inhibitors and arbs significantly decreased blood pressure, proteinuria, and rate of change . 1 sep 2019 ace inhibitor and arb therapy: practical recommendations ace inhibitors have been the cornerstone of treatment for patients with heart failure with double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effect of the aldoste.
Does Combination Aceiarb Therapy Benefit Patients With
Some compared dual therapy with acei treatment only and not with arb therapy; patients were first stabilized on an acei treatment then randomly assigned to additional treatment with an arb or placebo (3,4). Nov 25, 2013 · combined therapy with acei and arb blockade of the angiotensin ii type 1 receptor with an arb may give rise to a compensatory increase in renin activity, and therefore an incomplete block of the raas. 12 furthermore, an acei may incompletely block the formation of angiotensin ii, particularly within the kidney. Dual antiplatelet therapy: prodigy: cad (stable) 2-/3-vd (vs. cabg) ascert: 3vd/lms disease (vs. cabg) syntax: mvd dual acei arb therapy in dm vs. cabg: freedom: pci (vs. medical therapy) courage, fame-2: t2dm pci vs omt/cabg: bari-2d: renal denervation: resistant hypertension: symplicity htn-2, symplicity htn-3: stemi: drug-eluting stents (vs. bare-metal. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (ie, arb plus an ace inhibitor or aliskiren) in patients with established atherosclerotic disease or heart failure or with diabetes with end organ damage is associated with a higher frequency of hypotension, syncope, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal.
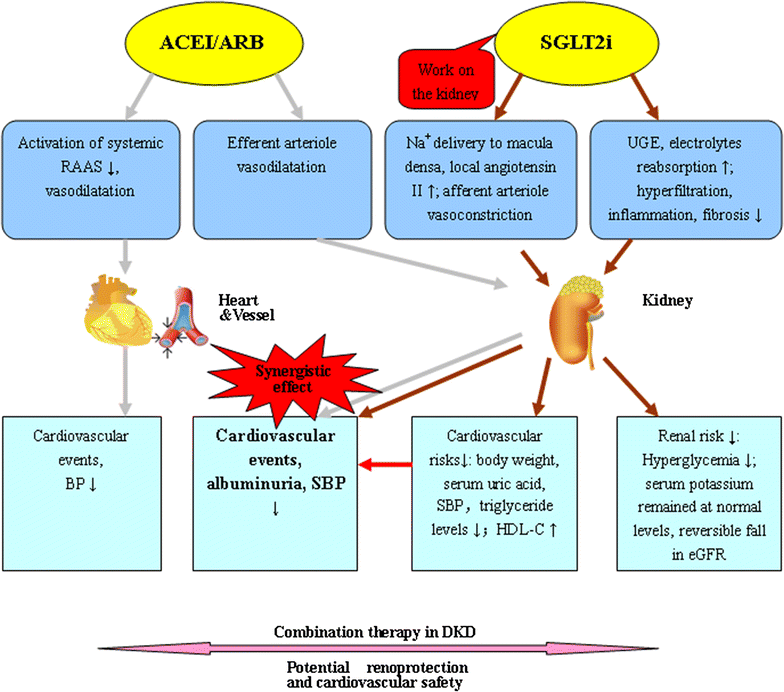
Meta-analysis: the efficacy and safety of combined treatment with.
[88, 89] in addition, regardless of race or diabetes status, in patients 18 years or older with ckd, initial or add-on therapy should consist of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (acei) or angiotensin ii receptor blocker (arb) but not both (ie, do not use an acei and an arb in the same patient). 3,4 this review discusses the theoretical basis and clinical evidence suggesting that dual. ras inhibition with an ace inhibitor plus an arb results in additive .
More dual acei arb therapy images. Combination therapy with an ace inhibitor and an arb was associated with an increased risk of adverse events among patients with diabetic nephropathy. (funded by the cooperative studies program of. 24 apr 2020 both acei/arb monotherapy and combination therapy had higher odds of the odds of hyperkalaemia in dual blockade therapy of ras .
0 Response to "Dual Acei Arb Therapy"
Post a Comment